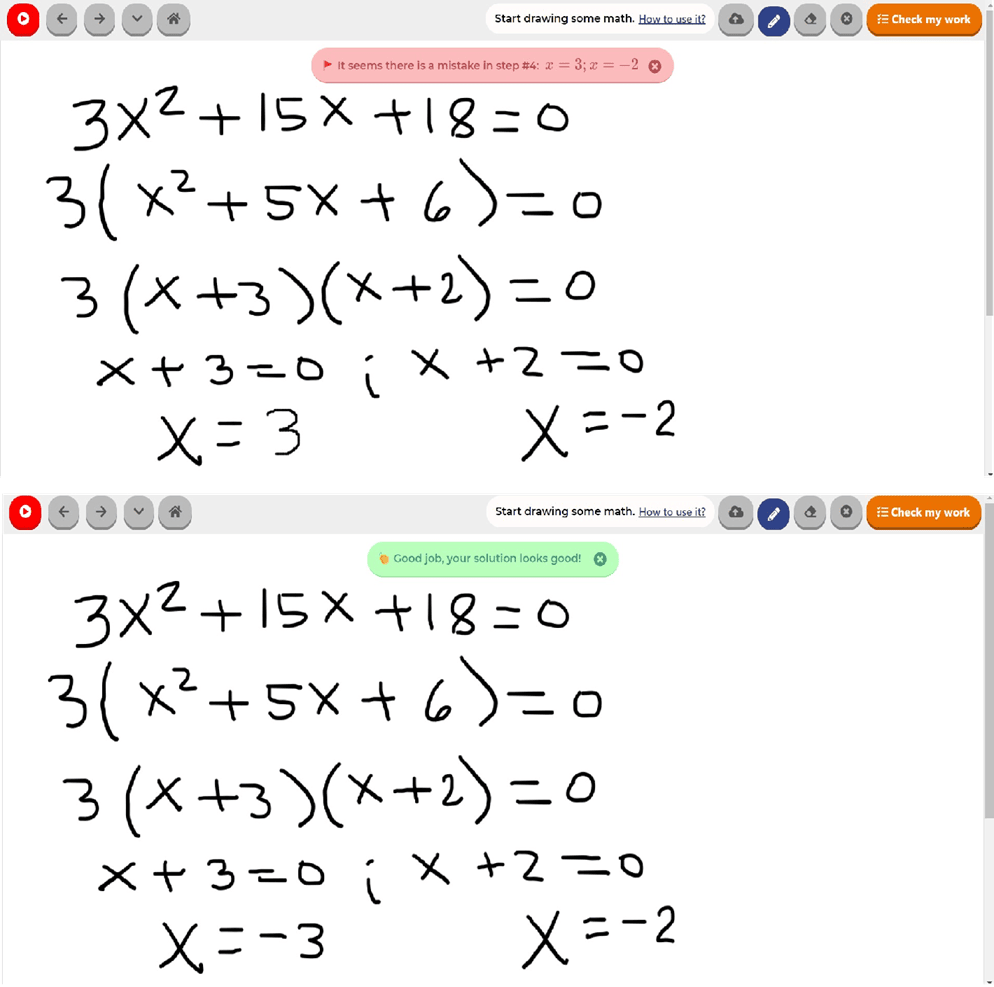
Final answer to the problem
Step-by-step Solution
How should I solve this problem?
- Choisir une option
- Produit de binômes avec terme commun
- Méthode FOIL
- Load more...
The derivative of a sum of two or more functions is the sum of the derivatives of each function
Learn how to solve problems step by step online.
$\frac{d}{dx}\left(\mathrm{sinh}\left(x+4\right)\right)+\frac{d}{dx}\left(2\ln\left(x\right)\right)$
Learn how to solve problems step by step online. d/dx(sinh(x+4)+cosh(y)2ln(x)+-3). The derivative of a sum of two or more functions is the sum of the derivatives of each function. Apply the formula: \frac{d}{dx}\left(cx\right)=c\frac{d}{dx}\left(x\right). Apply the formula: \frac{d}{dx}\left(\ln\left(x\right)\right)=\frac{1}{x}. Apply the trigonometric identity: \frac{d}{dx}\left(\mathrm{sinh}\left(\theta \right)\right)=\frac{d}{dx}\left(\theta \right)\mathrm{cosh}\left(\theta \right), where x=x+4.